Radiant heat in a home is a heating system that supplies heat directly to the walls, floors, or ceiling, rather than using air ducts or baseboard heating. This type of heating relies on the transfer of heat through radiation, providing a more comfortable and efficient way to heat a living space.
Radiant heat systems can be powered by electricity or natural gas, and they offer several benefits such as energy savings, consistent warmth, and improved indoor air quality. However, installation costs can be higher, especially if retrofitting is required. Overall, radiant heat is a popular choice for homeowners seeking a reliable and effective heating solution.
Essential Mechanism Of Radiant Heat
Radiant heat is an essential mechanism of heating in homes that provides warmth and comfort by directly transferring heat from a warm surface to the objects and people in the room. Unlike traditional heating methods which rely on convection to warm the air, radiant heat works by emitting electromagnetic waves that travel through space and are absorbed by objects, including furniture, floors, and even our bodies. This makes radiant heat not only efficient but also more comfortable, as it eliminates the circulation of dust particles and reduces air movement, making it an ideal heating solution for individuals with allergies or respiratory sensitivities.
Principle Behind Radiant Heating Systems
Radiant heating systems operate based on the principle of electromagnetic radiation. When a warm surface, such as a heated floor or a radiant panel, is present in a room, it emits infrared radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves. These waves travel through the room, without heating the air directly, until they come into contact with cooler surfaces, objects, or people. Upon contact, the warmth is transferred from the warm surface to the cooler objects, creating a comfortable and evenly distributed heat in the space.
Radiant Versus Convectional Heating Methods
Unlike traditional convectional heating methods that rely on warming the air in a room, radiant heating offers a more efficient and even heat distribution. In convectional heating, warm air rises and cool air sinks, creating temperature differences and often resulting in inconsistent heating. Radiant heat, on the other hand, directly heats objects and surfaces, minimizing temperature variations and providing a more consistent and comfortable warmth throughout the space. Additionally, radiant heat can be localized, allowing for zoned heating systems that provide customized comfort and energy savings.
The Science Of Radiation In Home Heating
Understanding the science behind radiation in home heating is crucial to fully appreciate the benefits of radiant heat. Radiation is an electromagnetic phenomenon that occurs when heat is emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves. These waves travel through empty space until they interact with cooler surfaces. When the waves come into contact with objects, their energy is absorbed and converted into heat. This heat transfer process creates a comfortable and efficient heating system that eliminates the need for forced air circulation and reduces energy consumption.
Radiant Heat Systems Explained
When it comes to heating your home, radiant heat systems offer a unique and efficient solution. Unlike traditional forced-air systems that blow hot air into a room, radiant heat warms the objects and surfaces in a space, providing a more comfortable and even heat distribution. In this article, we will explore the different types of radiant heating systems and how they work.
Types Of Radiant Heating Systems
Electric Radiant Floors
One type of radiant heating system is electric radiant floors. These systems consist of heating elements, typically cables or mats, installed directly under the flooring material. When electricity passes through these elements, they generate heat, warming the floor and radiating heat upwards.
Electric radiant floors are commonly used in bathrooms, kitchens, and other small areas where individual control is desired. They are easy to install and can be retrofitted into existing homes as well. Additionally, electric radiant floors offer quick and responsive heating, allowing you to enjoy the warmth in a matter of minutes.
Hydronic Radiant Floors
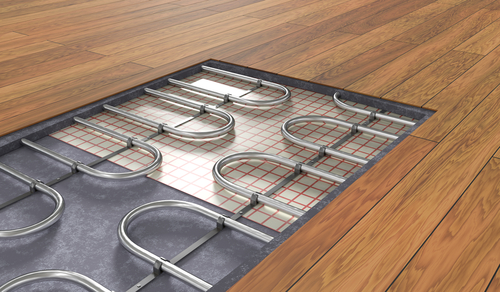
Another popular choice is hydronic radiant floors, which utilize a system of pipes filled with hot water or a mix of water and antifreeze. These pipes are installed under the floor and connected to a boiler, heat pump, or solar hot water system. The heated liquid circulates through the pipes, effectively transferring the heat to the floor surface.
Hydronic radiant floors provide efficient and consistent heating throughout the room. They can be used with various floor coverings, such as tile, hardwood, or carpet. Additionally, these systems are energy-efficient, as the water can be heated by renewable sources.
Radiant Panels And Their Place In Heating
In addition to radiant floors, there are also radiant panels that can be used for heating purposes. These panels are typically installed on walls or ceilings and use either electricity or hot water to emit radiant heat. They are an excellent choice for rooms with limited floor space or where floor installation is not feasible.
Radiant panels offer a quick and localized heating solution. They are often used in commercial buildings, offices, or even in residential spaces to provide supplemental heat. These panels are available in various sizes and designs, allowing for flexibility in installation and aesthetics.
In conclusion, radiant heat systems, whether through electric or hydronic floors or with the use of radiant panels, offer a comfortable and efficient heating option for your home. Consider these systems to experience the benefits of radiant heat and enjoy a cozy and evenly heated living space.
Installing ‘what Is Radiant Heat In A Home’
Radiant heat is a cost-effective and efficient way to keep your home warm during the colder months. By using a heating method that involves warm water flowing through pipes installed beneath the floor, you can enjoy a comfortable and cozy living space without the need for bulky radiators or ductwork.
Assessing Your Home For Radiant Heat Installation
Before installing a radiant heating system in your home, it is essential to assess whether your home is suitable for this type of heating. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial for the efficiency of radiant heat. Assess your home’s insulation to ensure it meets the recommended standards. Poor insulation can result in heat loss and lower energy efficiency.
- Subfloor type: The type of subfloor in your home will determine the installation method for radiant heat. Concrete subfloors are common for in-floor systems, while electric systems can be installed under different flooring types.
- Existing flooring: If you have existing flooring, it may need to be removed to install the radiant heating system. This can add to the installation costs, so factor this in during your assessment.
- Heating needs: Consider your heating needs and the specific areas in your home where you want to install radiant heat. This will help determine the size and capacity of the system you need.
Step-by-step Installation Processes
Once you have assessed your home and determined that radiant heat is suitable, you can proceed with the installation. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Choose the heating system: Select the type of radiant heating system that best suits your needs, such as hydronic or electric.
- Prepare the subfloor: If installing in-floor radiant heat, prepare the subfloor by leveling it and ensuring it is clean and free of debris.
- Install insulation: If necessary, install insulation to prevent heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
- Lay the heating elements: Depending on the system you chose, lay the heating elements evenly across the subfloor or attach them to the underside of the existing flooring.
- Connect the system: If using a hydronic system, connect the pipes to the boiler or water heater. If using an electric system, connect the heating elements to the power source.
- Cover and finish: Finally, cover the heating elements with a suitable flooring material, ensuring proper installation and finishing touches.
Key Considerations For Effective Setup
When installing radiant heat in your home, there are a few key considerations to keep in mind:
- System capacity: Ensure that the capacity of the radiant heating system matches the heating requirements of the specific area to be heated.
- Zoning: Consider dividing your home into multiple zones to have better control over the temperature and optimize energy usage.
- Thermostat placement: Install thermostats strategically to accurately monitor and control the temperature in each zone.
- Maintenance access: Plan for easy access to the system for routine maintenance and any necessary repairs.
By assessing your home, following the step-by-step installation process, and considering these key factors, you can achieve an effective and efficient setup for radiant heat in your home.
The ‘how’ Of Radiant Heating Regulation
Radiant heat is a popular heating system option for homeowners due to its efficient and comfortable nature. But how exactly is radiant heat regulated in a home? In this section, we will explore the various methods and options for controlling the distribution of radiant heat, zoning advantages, and thermostat options for radiant heat systems.
Controlling Radiant Heat Distribution
Controlling the distribution of radiant heat in a home is crucial for achieving optimal comfort and energy efficiency. One of the primary ways to regulate the distribution is by utilizing different flooring materials. Materials such as tile, concrete, or stone are excellent conductors of heat, allowing for efficient transfer from the heating source to the living space. On the other hand, carpet or wood flooring may impede the heat transfer, requiring additional measures to ensure even distribution.
Another important factor in controlling radiant heat distribution is the choice of insulation. Properly insulating the floor, walls, and ceilings helps minimize heat loss and ensures that the heat is directed towards the living areas. This not only enhances comfort but also reduces energy consumption, resulting in cost savings for homeowners.
Zoning And Its Advantages
Zoning is a key element in regulating radiant heat in a home. It allows homeowners to control the temperature in different areas or zones independently, based on their specific usage requirements. This means that each zone can have its own thermostat, allowing for personalized heating preferences and energy savings.
For example, bedrooms can be set to a lower temperature during the night when they are not in use, while the living room and kitchen can be maintained at a comfortable temperature throughout the day. Zoning not only provides flexibility but also reduces energy waste by avoiding overheating or cooling unoccupied areas.
Thermostat Options For Radiant Heat Systems
Choosing the right thermostat for a radiant heat system is crucial to ensure precise temperature control and user-friendly operation. There are several options available, including:
- Manual thermostats: These basic thermostats allow for manual temperature adjustment and are suitable for homeowners who prefer a more hands-on approach.
- Programmable thermostats: These thermostats offer the ability to set different temperature profiles for specific times of the day or week. They are ideal for homeowners who want to automate their heating preferences and save energy.
- Smart thermostats: Smart thermostats are the latest trend in home heating control. They can be controlled remotely via mobile devices, learn user preferences, and adjust heating patterns accordingly. These thermostats offer advanced features such as energy usage monitoring and compatibility with home automation systems.
Evaluating The Performance And Efficiency
Radiant heat is a type of heating system that uses natural gas or electricity to heat components, such as floors or ceilings, which then radiate warmth throughout the home. This method is cost-effective and versatile, providing efficient and comfortable heating in any room.
Measuring The Efficiency Of Radiant Heat
When it comes to evaluating the performance and efficiency of radiant heat in a home, it is important to consider various factors. One of the key aspects to assess is the efficiency of the heating system. Measuring the efficiency of radiant heat can help homeowners determine how well their system is performing and whether any improvements can be made.Long-term Benefits And Energy Savings
Radiant heat systems offer several long-term benefits and energy savings. These systems work by directly heating the objects in a room, such as floors, walls, or ceilings, rather than heating the air. This not only ensures a more comfortable and consistent temperature throughout the space but also results in energy savings. By focusing on heating the objects, radiant heat systems can maintain a comfortable temperature with less energy consumption compared to traditional heating systems. Some of the key benefits of radiant heat include:- Improved energy efficiency
- Reduced energy bills
- Increased comfort levels
- Elimination of cold spots
- Quiet operation
- Improved air quality
Maintenance Tips For Radiant Heating Systems
To ensure the efficient operation and longevity of radiant heating systems, it is important to follow proper maintenance practices. Here are some maintenance tips for radiant heating systems:- Regularly inspect the system for any leaks or damage.
- Keep the area surrounding the heating elements clean and free from obstructions.
- Flush the system periodically to remove any buildup of sediment or mineral deposits.
- Check and replace any faulty thermostats or sensors.
- Ensure proper insulation to minimize heat loss.
- Consider professional maintenance checks on a regular basis.
Credit: www.santaenergy.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Radiant Heat In A Home
What Is The Downside Of Radiant Heat?
The downside of radiant heat is that it can be expensive to install if you have existing flooring that needs to be removed. However, there are options to install specially designed pads between floor joists to minimize costs.
What Are Examples Of Radiant Heat In A Home?
Radiant heat examples in a home include propane boilers, electric boilers, oil boilers, geo-thermal systems, and water heaters. These systems provide heat directly to the floor or panels in the wall/ceiling, using natural gas or electricity as a fuel source.
The heat is delivered through infrared radiation, making it efficient and comfortable.
Is Radiant Heat Expensive To Run?
Radiant heat is not expensive to run. It is a cost-effective heating option that uses either natural gas or electricity as fuel sources. The system efficiently heats the water that flows through the pipes, providing warmth directly to the floor or panels in the walls or ceiling of your home.
Is Radiant Heat Electric Or Gas?
Radiant heating systems can be powered by either natural gas or electricity. Electric systems heat components through electrical resistance, while gas systems require a boiler installation to heat the water that flows through the pipes of the system.
Conclusion
Radiant heat is an increasingly popular heating option in homes that offers several benefits. With its ability to provide consistent and even heat distribution, radiant heat creates a comfortable and cozy living environment. It also eliminates the need for bulky and unsightly heating systems, as the heat is emitted from beneath the floor or through panels in the walls or ceilings.
Additionally, radiant heat is energy efficient, reducing energy consumption and saving costs in the long run. Considering all these advantages, it’s no wonder that many homeowners are turning to radiant heat as a heating solution for their homes.

